Six Sigma is a methodology used to improve business processes. It reduces defects and errors. It increases quality and efficiency. It aims to achieve 99.9% quality perfection. It uses DMAIC structured approach.
The business world is buzzing about Six Sigma, and it’s because this data-driven approach to process improvement is fueling the success of Fortune 500 titans and industry leaders in real time. Companies like Amazon, Netflix, and Coca-Cola attribute a significant portion of their success to Six Sigma principles, with estimates suggesting a collective $427 billion in savings across implementing companies.
Indeed, Six Sigma’s impact isn’t limited to tech giants. Its adaptability makes it an invaluable tool across diverse industries. Manufacturers from automobiles to shoes, electronics to textiles, utilize Six Sigma to streamline operations and deliver top-notch products.
Interested in learning how Six Sigma can revolutionize your business? Read on to discover the DMAIC methodology, real-world success stories, and how to apply this powerful framework to achieve operational excellence.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a methodology used to improve business processes. It reduces defects and errors. It increases quality and efficiency. Basically, this aims for near-perfection. It achieves this with only 3.4 defects per million opportunities. It uses a structured approach called DMAIC. DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control. Companies like Motorola and General Electric use Six Sigma. It is applied in various industries. These include manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and services.
Quick Tip: Six Sigma can revolutionize software development and testing processes, ensuring higher quality and efficiency at every stage.
What are the 5 Key Principles of Six Sigma?
The Five Key Principles of Six Sigm are briefly explained as follows:
Focus on the Customer
The very first thing that Six Sigma prioritizes is thoroughly understanding and meeting all customer needs. For instance, a manufacturing company should conduct surveys or gather feedback to identify areas for improvement in their product quality or customer service.
Use of Data and Statistical Analysis
According to Six Sigma, organizations can uncover inefficiencies if they map out the value stream and analyzing data. For example, a hospital may use data analysis to identify bottlenecks in patient flow, which will ultimately lead to faster treatment and improved patient satisfaction.
Continuous Process Enhancement
Six Sigma affirms that it is essential to non-value-adding activities for businesses efficiency. Let’s say there’s a software development team. They can remove redundant steps to streamline their development process. This will ultimately result in faster delivery times and higher-quality software.
Keep the Ball Rolling
The next principle of Six Sigma is none other than continuous improvement. According to this, organizations must encourage ongoing engagement and innovation. For instance, an e-commerce company may regularly review customer feedback and conduct improvement projects. All this will help enhance their website’s user experience.
Ensure a Flexible and Responsive Ecosystem
You will surely agree that adaptability is quite important in today’s fully dynamic business environment. That’s why Six Sigma encourages organizations to embrace change. It helps to respond swiftly to market demands. For instance, if there’s a retail chain, it should effectively adjust its inventory management processes in response to changing consumer trends. This will help it minimize stockouts and optimize supply chain efficiency.
Don't know where to start your tech career?
We are here for you! Schedule a free call with our consultant for personalized advice on achieving your learning goals
What are the Levels of Six Sigma?
Six Sigma leverages a set of quality management methods, primarily based on empirical and statistical methods. This way it establishes a unique hierarchy of roles within an organization, including Champions, Black Belts, Green Belts, Yellow Belts, and others, each aligned with specific methodologies. Basically, a Six Sigma initiative within a company adheres to a predetermined series of steps. This aims to achieve specific, measurable goals such as “to cut down on the process cycle times, minimize the pollution, lower the costs, enhance the customer satisfaction, and boost the profits”.
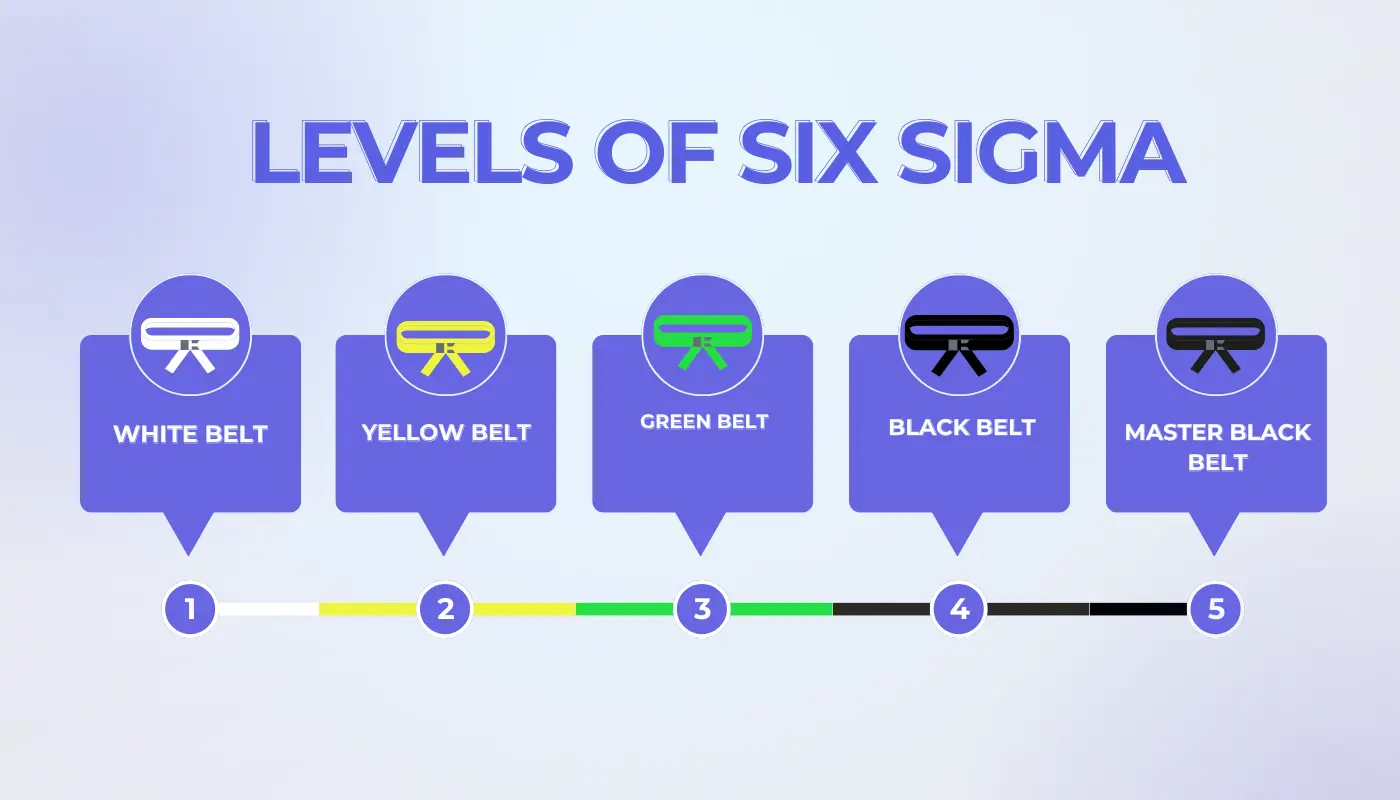
Let’s get to details of six sigma levels.
White Belt
A Six Sigma White Belt is the one that introduces the basics of Six Sigma to individuals at all organizational levels. This is done to foster a culture of continuous improvement. Their few-hour long training covers Six Sigma fundamentals and the DMAIC process. For example, an employee applies principles learned to streamline customer service processes, which ultimately, helps to enhance fficiency and satisfaction.
Yellow Belt
Yellow Belt certification provides a deeper understanding of Six Sigma, which is crucial for training individuals to support improvement projects actively. The training spans a few days, focusing on the DMAIC process and basic problem-solving tools. For example, a Yellow Belt in manufacturing helps identify causes of production defects, which in turn, leads to to quality improvements.
Green Belt
Green Belts are equipped to lead small projects or assist in larger ones, with comprehensive Six Sigma training that includes advanced analysis and project management. For instance, a Green Belt identifies and removes process bottlenecks to reduce order fulfilment cycle time and improve efficiency.
Black Belt
Black Belts are basically Six Sigma experts who lead significant projects, train Green Belts, and drive improvements aligned with organizational goals. The training involves in-depth study of statistical analysis and Six Sigma methodologies. For instance, a Black Belt leads a healthcare project to reduce medication errors. All while implementing changes that significantly enhance patient safety.
Master Black Belt
Master Black Belts are responsible for mentoring the Black and Green Belts along with overseeing Six Sigma’s strategic implementation while aligning projects with business objectives. They have extensive Six Sigma experience and a successful project leadership track record. For instance, a Master Black Belt coordinates global quality improvement projects across a multinational corporation. All while standardizing practices and boosting overall satisfaction and efficiency.
Tools and Techniques in Six Sigma
The Six Sigma approach uses a number of tools and techniques across its two main methodologies- DMAIC for improving existing processes and DMADV for creating new product or process designs.
The Six Sigma Methodology encompasses a suite of techniques designed to enhance process efficiency and quality, including:
- DMAIC- This stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, outlining a systematic approach to problem-solving that is structured and methodical.
- SIPOC- Standing for Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers, this tool helps in the visualization of process elements, all while facilitating a clearer understanding of the process flow.
- FMEA- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis is employed to preemptively identify potential points of failure and their consequential impacts, all just to foster a proactive approach to quality control.
- Control Charts- These tools are utilized for the ongoing monitoring of process performance, which in turn, allows or the detection of variances over time.
- Pareto Analysis- This is a strategic technique that aids in pinpointing the most significant factors within a dataset, which is based on the principle that a small number of causes often lead to a large portion of the effect.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)- This method applies statistical techniques to monitor and control a process. All while ensuring it operates at its maximum potential with minimal variation.
Whereas the Six Sigma Tools include the following:
- Problem Identification and Root Cause Analysis (Cause and Effect Analysis and 5 Whys)
- Process Mapping (Flow Chart, SIPOC Diagram, and Value Stream Mapping)
- Data Analysis (Pareto Chart, Histogram, Check Sheet, Scatter Plot, and Control Chart)
- Statistical Techniques (Hypothesis Testing and Design of Experiments (DOE))
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen and 5S System)
- Error Prevention (Poka-yoke, Failure Mode and Effects Analysis, Customer Focus, and Voice of the Customer)
The Six Sigma Methodology
The Six Sigma Methodology emphasizes to “reduce defects and enhance quality”. All while employing a structured approach encapsulated mainly by the DMAIC and DFSS (including DMADV and IDOV) processes. These methodologies are underpinned by statistical and empirical analysis, and ultimately, aim to improve processes and design quality into products and services from the outset. Here’s how each Six Sigma method works:
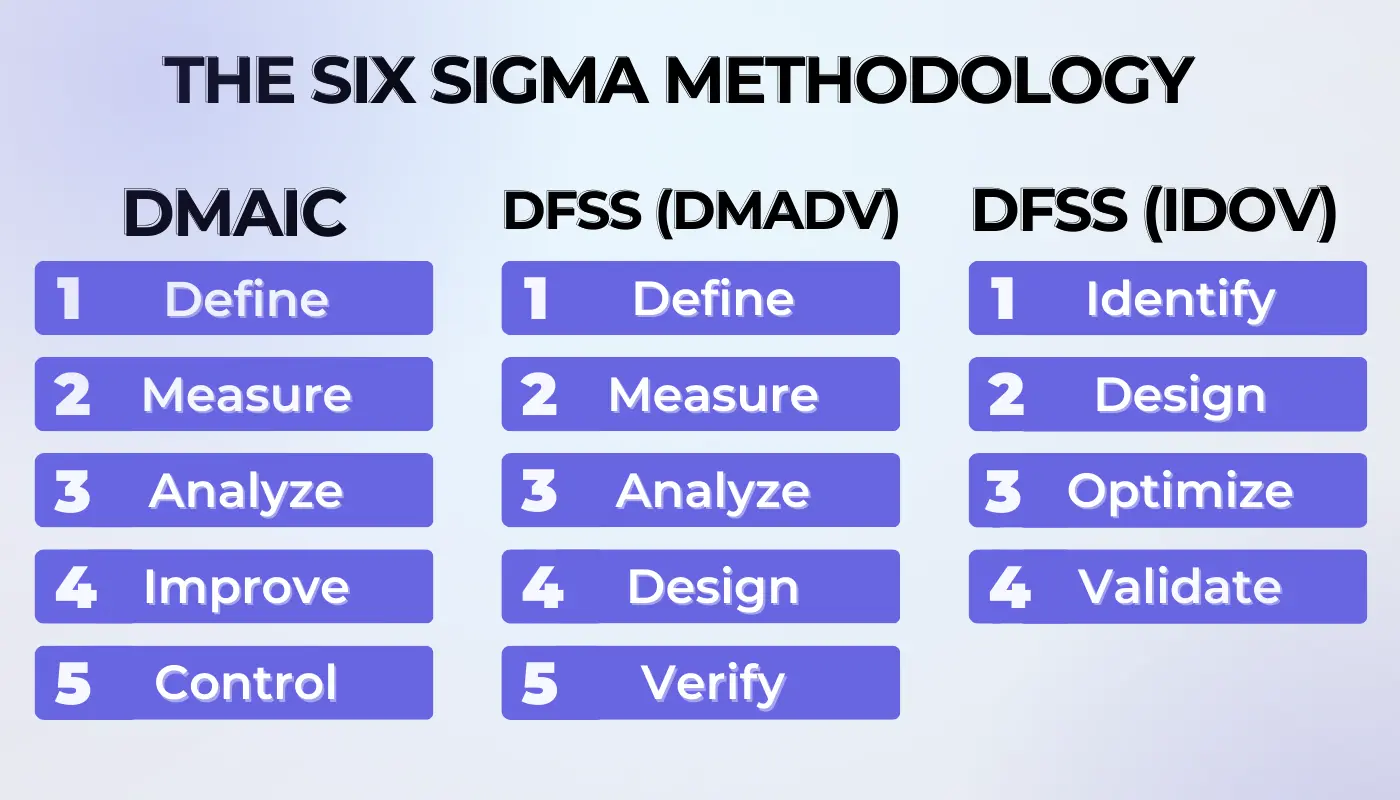
DMAIC
- Define- This requires organizations to establish the project goals, scope, and customer requirements. For example, a telecommunications company may identify frequent customer complaints about dropped calls as a problem to address.
- Measure- Next they need to collect data to establish baseline performance. For example, the company then may measure the current frequency and locations of dropped calls over a time period of a month.
- Analyze- Afterwards, they are required to identify the root causes of the defects. For example, the analysis then reveals that dropped calls primarily occur in densely populated areas, especially during peak hours.
- Improve- Once analysis is done, they need to thoroughly implement the solutions and in turn, mitigate the root causes. For example, then the company aims to upgrade its infrastructure in the target areas and optimize network capacity for improved performance.
- Control- After all, they need to put all mechanisms in place as this is important for sustaining the improvements. For example, the company then effectively sets up real-time monitoring to manage call traffic in an efficient manner and prevent future congestion.
DFSS (DMADV)
- Define- This means that organizations need to clearly state the project goals, all while considering customer needs and project objectives. For example, a car manufacturer aims to design a new, highly fuel-efficient vehicle.
- Measure- Next, they need to properly identify and measure characteristics critical to quality (CTQs), product capabilities, production process capability, and risks. For example, the manufacturer determines key customer requirements for fuel efficiency, reliability, and cost.
- Analyze- Moving forward, they are required to take a deep look and analyze the options to meet the customer needs and CTQs. For example, the design team analyzes various engine designs and materials to achieve high fuel efficiency and low production costs.
- Design- After the analysis part, they need to effectively design the new product or process, along with optimizing the design to meet customer needs and CTQs. For example, the team selects a hybrid engine design with lightweight materials to maximize fuel efficiency.
- Verify– Lastly, they are required to thoroughly test and verify the design to ensure it meets customer requirements and performance standards. For example, the prototypes are tested for fuel efficiency, performance in different conditions, and reliability over time.
DFSS (IDOV)
- Identify– This is where the companies need to properly recognize customer needs or demands and specifications for a new product or process they require. For example, a software company identifies a need for a new project management tool tailored for remote teams.
- Design- Once the identification process is completed, they need to create a detailed design that effectively meets the audience’s needs. For example, the design then would possibly include features for real-time collaboration, task tracking, and integration with existing tools.
- Optimize– Next, they are required to refine the design just to optimize performance and customer satisfaction. For example, user feedback on a beta version will then lead them to offer an improved interface design along with additional features for project reporting.
- Validate– In the end, they need to confirm that the design meets or possibly exceeds the original specifications. For example, the final product will then undergo rigorous testing, all just to show that it meets the specified needs with high reliability and user satisfaction.
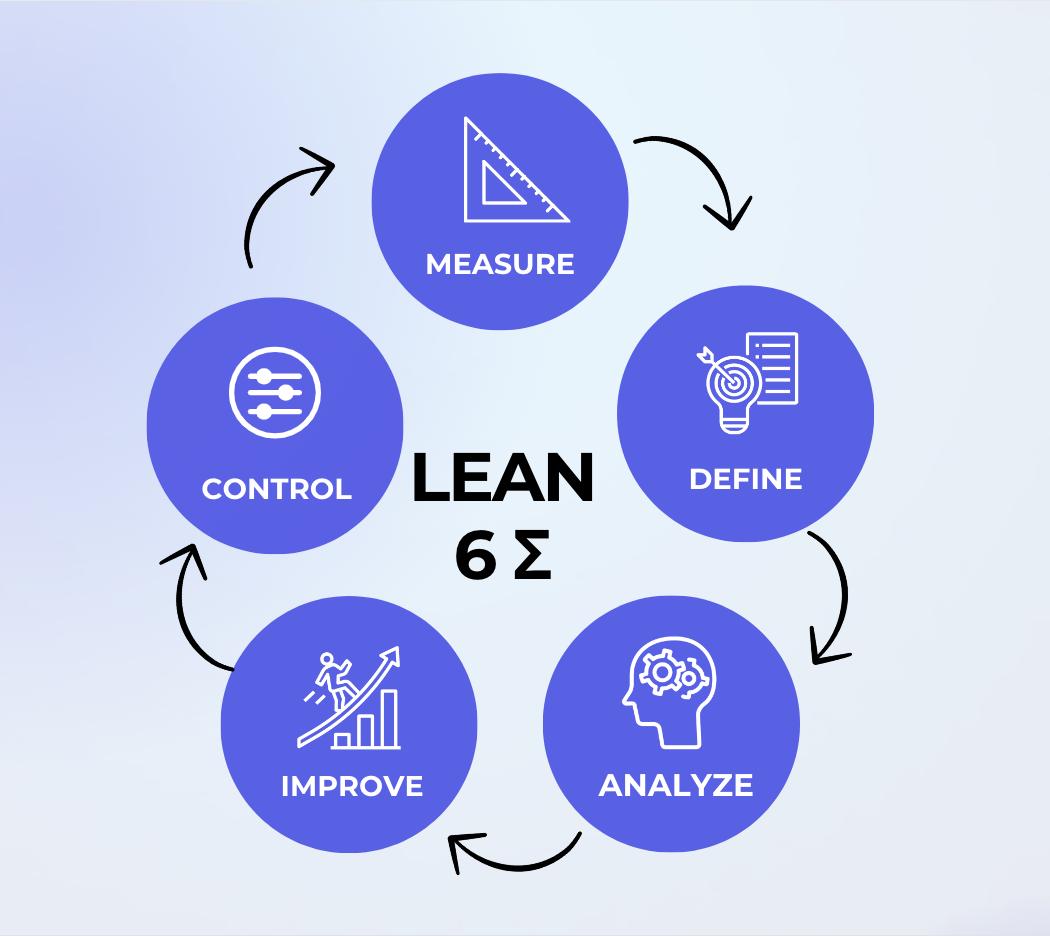
The Role of Six Sigma in Software Development
Six Sigma in software development focuses on improving the quality of software products and processes. All by identifying and eliminating defects, which in turn, minimizes variability and improves overall efficiency. It employs a data-driven approach to reduce bugs and enhance customer satisfaction. Ultimately, it helps ensure that the development process is as efficient and effective as possible.
Let’s consider a software development company dealing with project delays and quality issues. They can implement Six Sigma to overcome all this. Firstly, they will define their challenges and objectives. Next, the they’ll go through the measure phase during which crucial performance data will be collected. Following this, they will leverage Six Sigma tools for analysis and succeed in pinpointing the root causes of inefficiencies. The subsequent improvements will include refining testing methods and optimizing team workflows. Finally, a control phase will ensure these gains are sustained. All this will minimize the bugs and ensure higher customer satisfaction along with a more streamlined project timeline. This strategic shift will rescue the current project as well as level-up the company’s overall approach to quality and efficiency.
Final Words
Six Sigma revolutionizes business processes at a global level, all by aiming for near-perfect quality and reducing defects to a mere 3.4 per million. It effectively blends data-driven rigor with Lean efficiency, streamlining operations and cutting waste. From White to Master Black Belt, it offers a path for professionals to lead transformative improvements. All while making it an essential strategy for achieving unparalleled excellence in any industry.